Roger Solé, Conrad Ferrer, Oriol Aviñó-Salvadó, Xavier Jordà, Xavier Perpiñà.
IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement
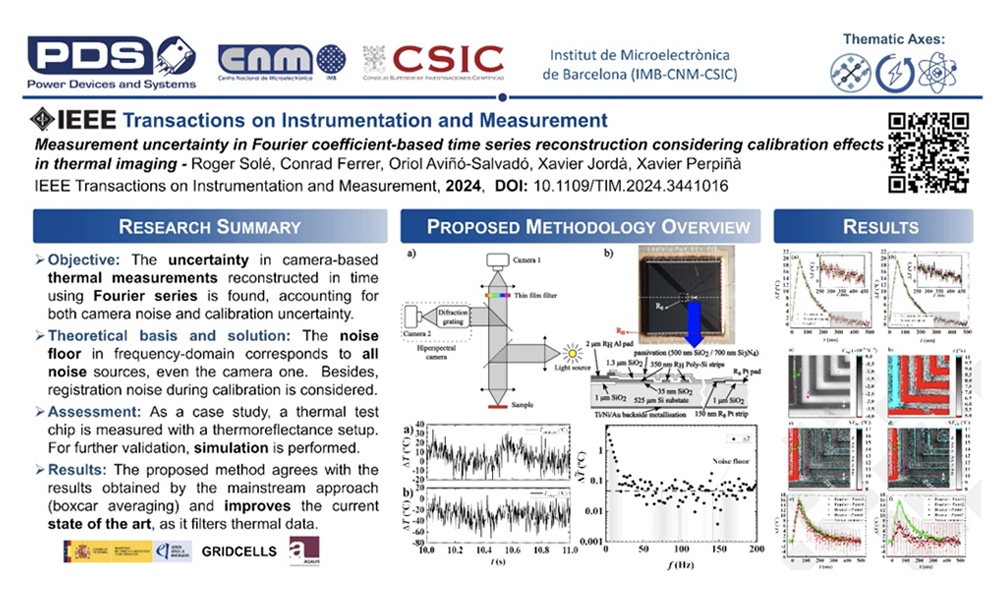
A robust methodology is proposed for determining and assessing measurement uncertainties in thermal imaging systems when the Fourier coefficient-based time-reconstructed method is used. This comprehensive approach addresses factors such as camera-induced noise, setup-related errors, and data postprocessing strategies. As a case study, this methodology is applied to measure a thermal test chip (TTC) using a thermo-reflectance (TR) setup. The results are validated with the stroboscopic boxcar averaging technique. This study yields valuable insights. The camera introduces a Rayleigh-distributed white noise, which is extracted in both postprocessing methods. Image registration mitigates thermo-mechanical displacements during calibration effectively. Key uncertainties are identified for each method. Registration and calibration errors remain under 5%, with camera noise contributing only 0.5° C of measurement uncertainty. These uncertainties allow for accurate thermal measurements with a precision of 2° C and preserving a high spatial resolution ( ∼1 μ m).
Link DOI: 10.1109/TIM.2024.3441016

This Fourier-based thermal imaging methodology is impressive! The sub-5% uncertainty across calibration errors mirrors the precision engineering I’ve seen in gaming platforms. Just as gogojili download apk systems maintain accuracy under heavy loads, your 2°C precision with high spatial resolution sets a new benchmark. Excellent validation approach!