X. Perpiñà, M. Vellvehi, R. J. Werkhoven,, J. Jakovenko, J. M. G. Kunen, P. Bancken, P. J. Bolt and X. Jordà
IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, early acces.
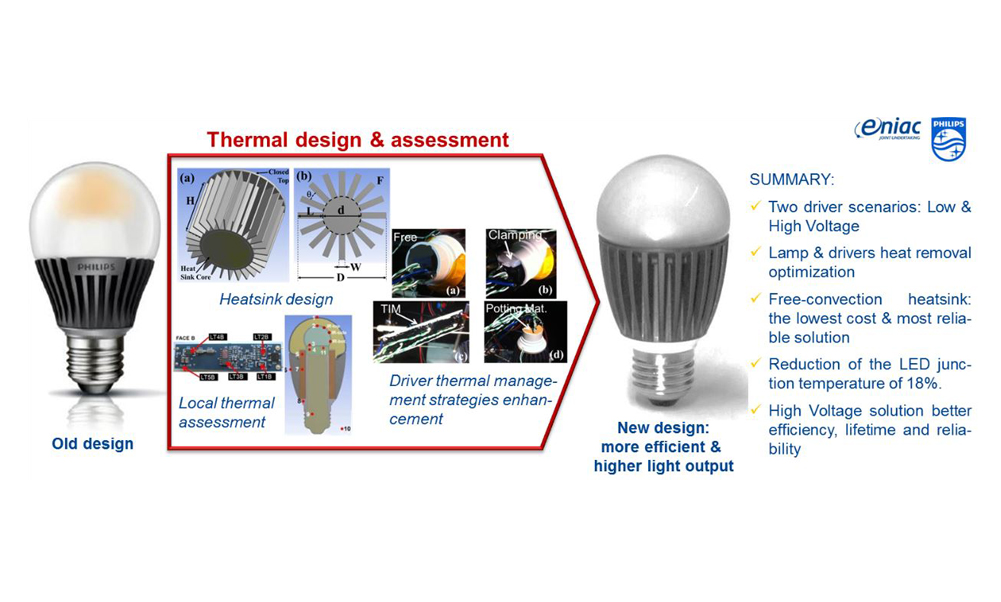
Several thermal management strategies for LED drivers designed for high lumen retrofit LED lamps are studied by simulation and experimentation means. Depending on the driver output, two scenarios are analyzed: Low Voltage-High Current (18V-620mA) and High Voltage-Low Current (110V-85mA). Experiments (infrared thermography and thermocouples) and multiscale simulation approaches are used to assist both the lamp and driver board thermal design, as well as the driver proper integration in the lighting system. As a result, a heatsink based on an Aluminum hollow cylinder with polymer axial fins is designed and evaluated. The heatsink assessement is carried out with an LED board, in which the LED junction temperature is modeled and extracted by monitoring the LED board backside temperature. Additional experimentation to better integrate the driver is performed aiming at reducing the contact thermal resistance between the driver and the heatsink and improving the heat removal in the driver housing by including a material with a high thermal conductivity (i.e., dry silica sand or magnesium oxide powder). The proposed solution reduces the LED junction temperature up to 18% with respect to a reference lamp, whereas both drivers depict working temperatures around or below 125°C, when a working temperature of 90°C is considered.
Link DOI: doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2018.2853119